Revolutionize Your Operations: The Complete Process Flow and Equipment Configuration of Slaked Lime Production Line Equipment
Slaked lime, that is, calcium hydroxide, is an extremely important inorganic chemical raw material, which is widely used in many fields such as construction, environmental protection, and chemical industry. As the core facility for producing calcium hydroxide, the process flow and equipment configuration of the slaked lime production line play a decisive role in product quality and output. This article will give a detailed introduction to the process flow and equipment configuration of the slaked lime production line to provide a reference for related industries.
Process flow of slaked lime production line
Raw material preparation
The first step is to crush and screen the raw materials to obtain raw materials with uniform particle size. Common raw materials include limestone, dolomite, etc.
Raw material digestion
Mix the crushed and screened raw materials with an appropriate amount of water, and carry out digestion reaction in the digester to produce lime milk. During the digestion process, the temperature and pH value need to be controlled to ensure the quality of lime milk.
Purification of lime milk
There are small particles and impurities that are not completely digested in the lime milk, which must be purified. Common purification methods include filtration and sedimentation.
Aging of lime milk
Aging refers to the process of promoting the full reaction of lime milk under specific temperature and pressure conditions to improve its quality. Aging lime milk is more stable and more conducive to subsequent processing.
Dehydration of lime milk
Dehydration aims to remove water from lime milk to obtain solid calcium hydroxide. Common dehydration methods include natural drying and mechanical dehydration.
Finished product packaging: Calcium hydroxide after dehydration needs to be screened and packaged to meet market demand.
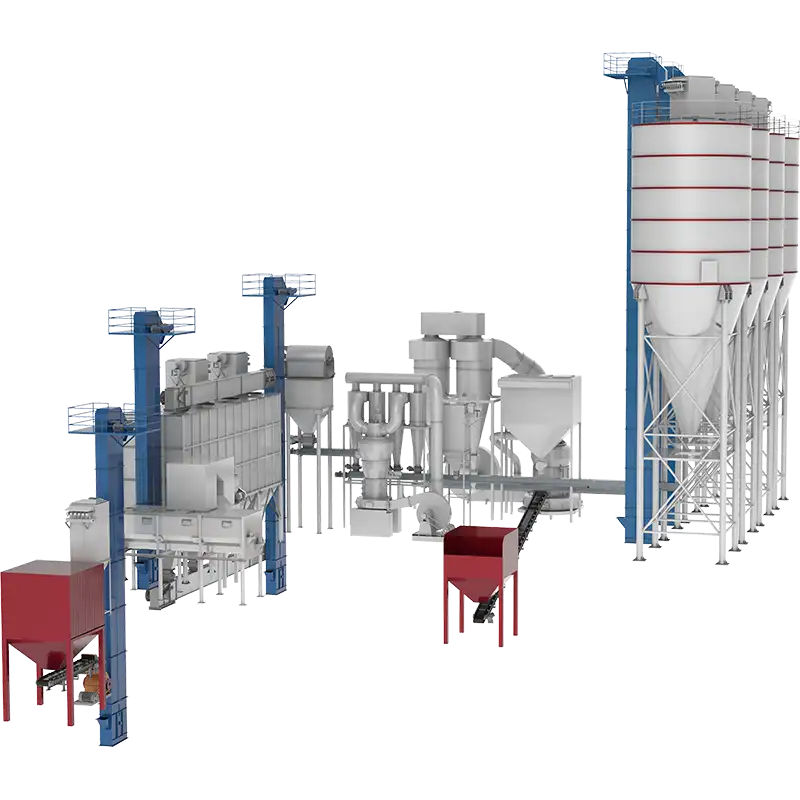
Equipment configuration of slaked lime production line
Raw Material Preparation
Limestone, mainly composed of calcium carbonate, is selected as the raw material. Equipment such as jaw crushers is used to crush large pieces of limestone to an appropriate particle size, usually 30 – 50mm, and then screening is carried out to remove impurities.
Calcination (Preparation of Quicklime)
Either a rotary kiln or a shaft kiln can be adopted. Under high temperature of 900 – 1100℃, calcium carbonate decomposes into calcium oxide (quicklime) and carbon dioxide. The reaction formula is: CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂↑.
Digestion (Slaking Reaction)
With the help of a digester (or slaker), quicklime and water are mixed in proportion, and a violent exothermic reaction occurs to generate calcium hydroxide (slaked lime). The reaction formula is: CaO + H₂O → Ca(OH)₂ + heat. It is necessary to strictly control the water volume, temperature and stirring speed to prevent caking or over – digestion.
Aging and Refining
The digested slurry is left to stand and age in the aging tank for 24 – 48 hours to improve the reaction completeness. Subsequently, un – digested particles and impurities are removed through hydrocyclones or vibrating screens.
Dewatering and Drying
Plate – and – frame filter presses or centrifuges are used to reduce the moisture content of the slurry to 30% – 40%. If a powdered product is required, a drum dryer or flash dryer can be used to further reduce the moisture content to less than 2%.
Grinding and Classification
Raymond mills, ball mills or vertical mills are used to grind the lumpy slaked lime to the target fineness of 80 – 325 mesh. The product is screened by an air classifier, and coarse particles are returned for re – grinding.
Packaging and Storage
The packaging forms include valve – bottom bags (25 – 50kg), ton bags or bulk tank trucks. It needs to be stored in a moisture – proof and air – tight environment to prevent caking or carbonation.
Environmental Protection and Quality Control
- Dust Control: Pulse – jet bag filters are used to treat the dust generated in the crushing and grinding processes.
- Wastewater Treatment: The digestion wastewater is recycled through sedimentation tanks.
- Quality Control Points: In the calcination stage, the activity of quicklime (T60≥90%); in the digestion stage, the free water content ≤ 2%; for finished product inspection, fineness, whiteness and calcium hydroxide purity (≥90%) are concerned.



